How to Remove or Edit robots.txt File from Website?

Your robots.txt file is massively important for your website. It references your website on Google, and on other major search engines, as well as on other websites. It’s located in the root of your web server and this file instructs robots to crawl (or not to crawl) your site, and what folders it should index, as well as what folders it shouldn’t index. Many people need help editing this, as it’s an intricate bit of web design, and many people find trouble with it. So, how do you remove or edit your robots.txt from a website?
The robots.txt file is located in the root directory of your web hosting folder. You can usually find this in /public_html/ and you can remove it or delete it using: FTP, SFTP, SSH, WebDev, or with WordPress (that’s using a robots.txt WP plugin). Many sites also offer the editing of robots.txt in their settings.
robots.txt file is very important for your website, so you should think before deleting it. For this reason, we’ll be researching exactly what it’s used for, how to remove it, how to edit it, and how to test it in your search console. You’d be doing yourself a great injustice to delete a file that you truly need, so read the article ahead to properly understand exactly why you need the robots.txt file and how to edit it and remove it. Let’s get started!
Should I Have a robots.txt File?
“A robots.txt file tells search engine crawlers which pages or files the crawler can or can’t request from your site. This is used mainly to avoid overloading your site with requests; it is not a mechanism for keeping a web page out of Google.” – this quote is the definition of robots.txt files from Google.
To be as accurate as possible, we’ll strictly use Google’s definitions and explanations when it comes to robots.txt.
“For web pages, robots.txt can be used to manage crawling traffic if you think your server will be overwhelmed by requests from Google’s crawler, or to avoid crawling unimportant or similar pages on your site.” – this means that you shouldn’t use robots.txt to hide your site(s) from Google’s search engine. Your website can still appear in search results, even if it’s blocked with a robots.txt file.
When it comes to media files, you can use robots.txt to manage crawl traffic, and also to prevent image, video, and audio files from appearing in Google search results.
With resource files, you can use robots.txt to block resource files such as unimportant image, script, or style files, if you think that pages loaded without these resources will not be significantly affected by the loss. However, there’s a possibility that this will make the page harder for Google’s crawler to understand, and if this is the case, the absence of the resource files is harmful for your site, as Google won’t do a good job of analyzing pages that depend on those resources.
Put simply, here are the reasons that you might want to keep your robots.txt file:
– you want to block certain content on your website from search engines
– you’re still developing a live site, and you don’t want to index it on search engines until it’s finished
– you want to fine-tune access to your site from reputable bots and crawlers
– the paid links and advertisements you’re using need special instructions for bots
– your robots.txt helps you follow certain Google’s guidelines
Reasons you might want to edit or delete your robots.txt file:
– you want everything indexed since your site is simple and error-free
– you don’t have any files that you want or need to be blocked from search engines
– none of the situations described above are something that you find yourself in
How to Remove a robots.txt File from Website?
Firstly, many website designs allow you to find your robots.txt file under the settings tab, so that’s what you want to check first. Go to your settings tab and see if your robots.txt file is there.
There are other methods, as well, even though the method described above will most likely be enough.
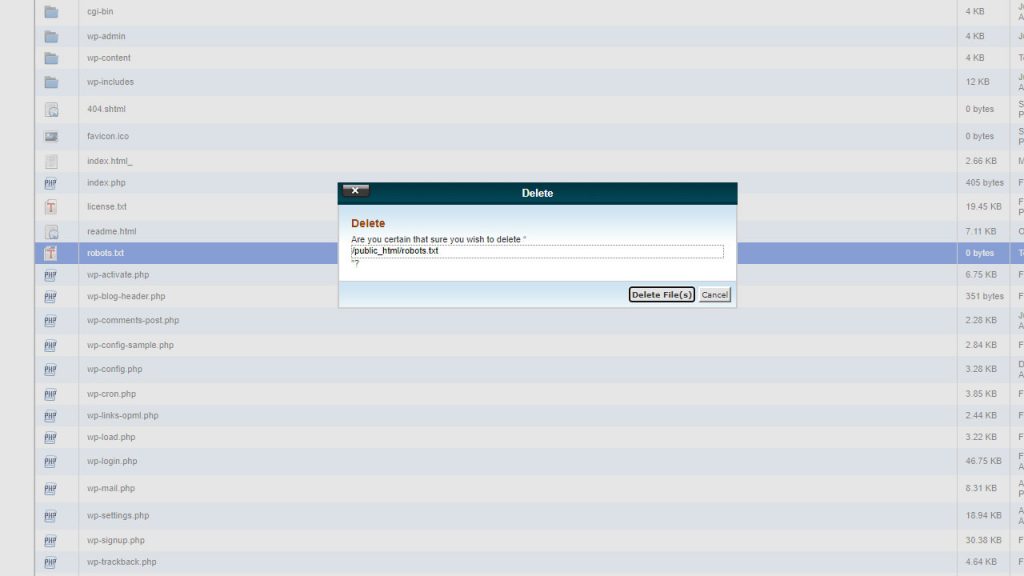
Try logging on to your hosting account. Look for the cPanel, go to the files section, and choose file manager. You can browse your directory and delete your files from there. Maybe it’d be better to just rename it to old_robots.txt – that way, it won’t be functional anymore, but you won’t be losing the file, in case you need it in the future.
If you’re using WordPress, then it’s a whole different story. WordPress generates new, updated robots.txt files periodically. There isn’t a physical file on the webserver that you can just delete and you can’t generate a new file on request. You should disable your robots.txt module, but if your robots.txt file is still accessible, then check the root folder of your web server using FTP to see if there’s a robots.txt file there. If you find one – delete it.
This should cover everything you need to know about deleting your robots.txt file. If you still can’t find the solution to your problem, then you should definitely contact your provider, as their support offices will surely know what’s going on and help you solve it.
How to Edit a robots.txt File on a Website?
Editing your site’s robots.txt file is an advanced feature, and after doing it, you may face some difficulty with your site’s pages being listed properly.
Once again, most providers ensure that you can access your robots.txt via settings.
Go to your dashboard, and you’ll find your robots.txt either under Settings or under Marketing (sometimes Marketing and SEO, or just SEO). You’ll see a robots.txt file editor, access it and you’ll have complete power over your robots.txt. Just save the changes once you’re done and that’s it.
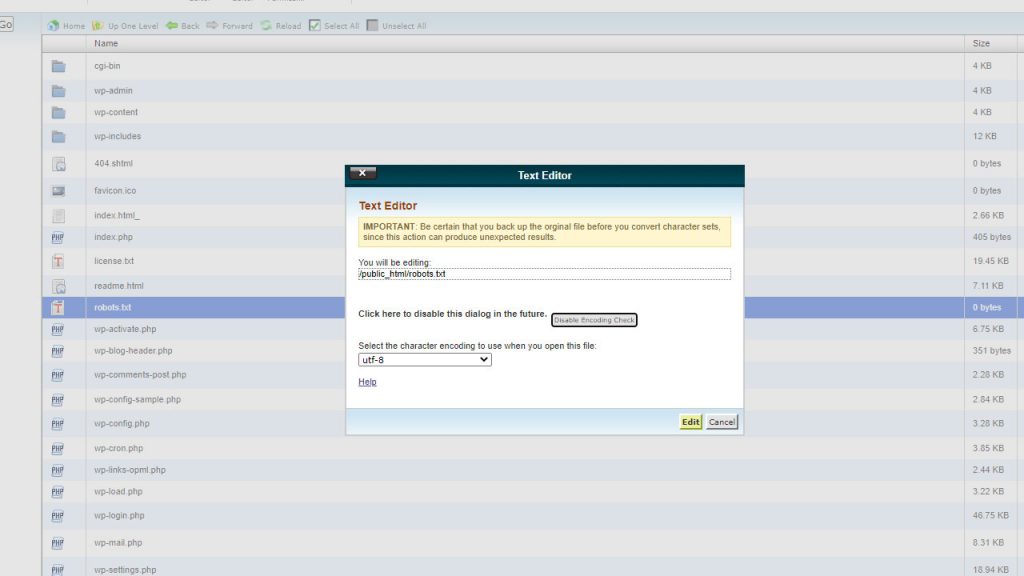
If you’re using WordPress, access SEO in the menu. Choose Tools and click on File Editor once you’re there. Make the changes to your file(s) and save the changes, it’s that easy.
You can also edit your file on your computer and upload it to your server. Use any text editor to create a file, and name it robots.txt. After doing what you wanted to do with it, upload the file to your server.
Here are a few tips for editing robots.txt:
– separate subdomains require separate robots
– make sure that your filename isn’t in caps: robots.txt is good, ROBOTS.TXT is no good
– fake or malicious crawlers are free to ignore the robots.txt file
– use the parameters “noindex, follow” to restrict indexation by search engine crawling robots – don’t use any other parameters for this purpose
– only one “Disallow:” line can be used for each specific URL
How to Test robots.txt in Search Console?
Open the tester tool for your site and scroll until you locate the highlighted syntax warnings and logic errors. You’ll see the number of syntax warnings and logic errors directly below the editor. Type the URL of a page on your site in the text box at the bottom of the page.
Choose what user-agent you want to simulate from the dropdown list to the right of the text box. Press ‘TEST’. Your test button will either read accepted or blocked, and you’ll find out if the entered URL is blocked from Google’s web crawlers.
Edit the file and test it again (if necessary). Copy the changes to the actual robots.txt file once you’re done.
Google actually has a testing tool in the search console for testing the robots.txt, so you won’t have to bother yourself with too much work.
Before choosing to delete or edit your robots.txt, make sure to test it out and see if it really is time to do that. Many changes or removals can be harmful for your SEO, especially if you do the wrong thing, so you should pay special attention to this. It’d be best to consult with an expert if you’re worried about your robots.txt file damaging your SEO and let them edit them accordingly. Most sites will let you edit it on-site, as your robots.txt is accessible through the main menu, and you’ll rarely have to edit it on your computer and only then upload it to the server (even though this is an option, as well).






