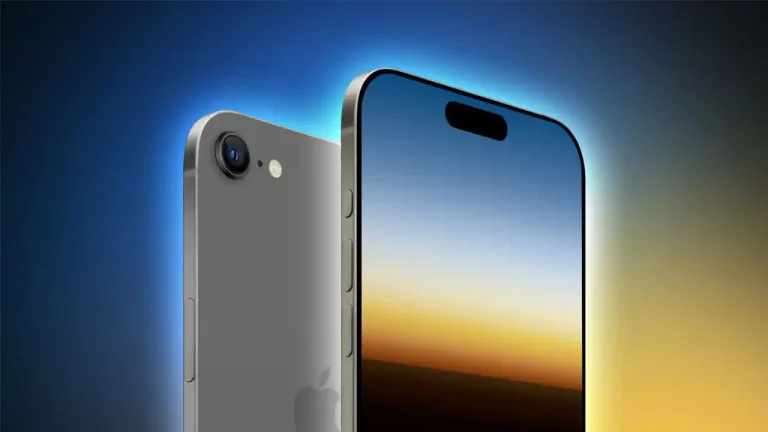
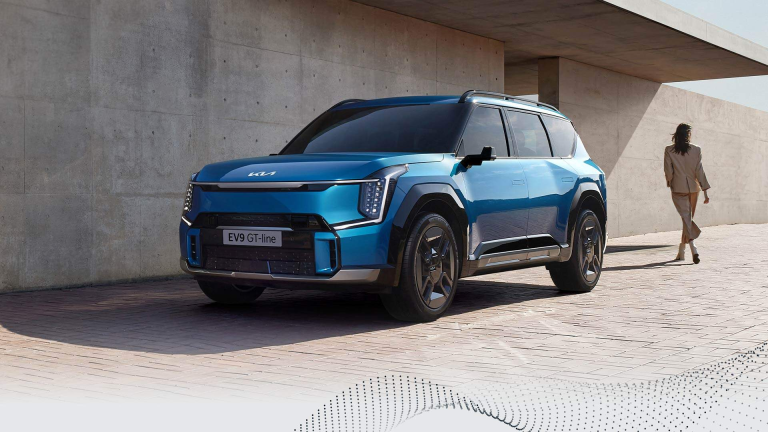
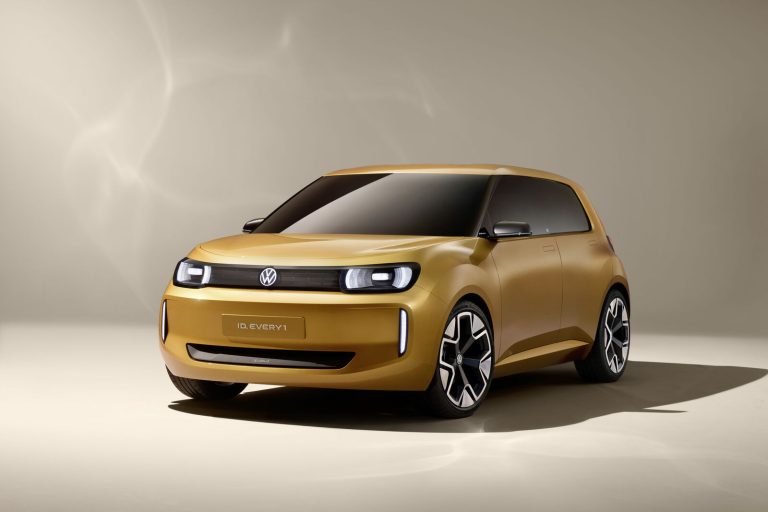
All the latest from the world of technology
… since 2020. We have the answer to your tech question!
Latest:
Follow us:
If you are looking to become a Kotlin developer, check out Thoughtsoncloud
If you want to see how fast can you click, check out Click Test and find out how fast you really are.