NASA Pinpoints Navigation Confusion as Likely Cause of Mars Helicopter Crash

Recent insights from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory and AeroVironment have shed light on the likely reasons behind the January 18th, 2024, crash of the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter.
The craft’s vision navigation system, designed to identify textured Martian surface features, encountered a challenge with a featureless, sandy area.
This confusion led to incorrect velocity estimates, causing Ingenuity to land harder than expected.
During its descent, the helicopter faced high horizontal velocities as it touched down, resulting in a hard impact against a sand ripple.
This sudden impact caused the helicopter to pitch and roll, leading to excessive strain on the spinning rotor blades.
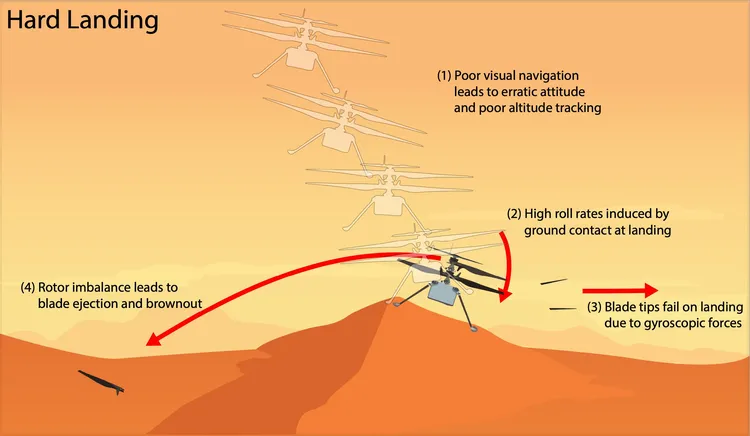
Illustration: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Initially, it was thought that the blades were damaged by contact with the Martian surface; however, further analysis suggested that they broke off due to the extreme forces from the rapid attitude change.
One rotor blade was found nearly 49 feet from where Ingenuity ended up. The crash also caused a temporary loss of communication due to vibrations in the damaged rotor system, which demanded too much power.
Communications were fortunately restored the following day. Despite being unable to fly again, Ingenuity still transmits useful weather and avionics test data to the Perseverance rover about once a week.
Ingenuity was initially expected to conduct just five flights over a month but impressively managed nearly three years of operation and over two hours of flight time across 72 flights. This data is proving invaluable to engineers designing future Red Planet aircraft and vehicles.
